- Details
- Category: Articles
 Offshore Wind Poised for Potential Boom
Offshore Wind Poised for Potential BoomAs the Biden administration prepares for unprecedented development in renewable generation, Asia-Pacific wind generation is hitting record level spend, and South Korea unveils seismic plans to build the world’s largest offshore wind farm, wind farm operators are positioning themselves to capitalise on this all-time high, gigawatt power generation fever.
By Gregory R. Wolfe, CEO / Chief Technology Officer and Co-Founder, Fischer Block, Inc., USA
- Details
- Category: Articles
 Impact of Wind Farms on Wind Speed and Capacity Factor
Impact of Wind Farms on Wind Speed and Capacity FactorOffshore wind farms are getting more attention as a source of renewable energy due to high and consistent offshore winds. These reliable offshore winds favour the construction of large offshore wind farms despite their high installation and operational costs. However, the deployment of such large offshore wind farms in proximity to each other, as planned in the North Sea, can significantly affect power generation and increase economic losses of the downstream wind farms.
By Naveed Akhtar, Scientist, Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon, Germany
- Details
- Category: Articles
A Brief Review of Methods and Requirements
 A consistent trend found in the manufacturing process of utility-size, horizontal-axis wind turbines throughout the years is the steady growth of the rotor diameter, which has led to a decreasing cost of wind energy conversion. However, while power conversion increases with the third power of the wind velocity, the aerodynamically generated noise may scale with the fifth or sixth power of the flow velocity. Thus, the noise associated with the ever-larger rotor diameter and higher local speeds due to increasing tower heights might impose limitations on the size of onshore-bound equipment in the future. This environmental restriction involves structural and material technical challenges already faced by the wind energy industry, which must meet challenging clean energy goals set by countries worldwide in order to fulfil greenhouse gas emissions limitations and global warming temperature limits proposed by the Paris Agreement and other subsequent sessions of the Conference of the Parties of the United Nations.
A consistent trend found in the manufacturing process of utility-size, horizontal-axis wind turbines throughout the years is the steady growth of the rotor diameter, which has led to a decreasing cost of wind energy conversion. However, while power conversion increases with the third power of the wind velocity, the aerodynamically generated noise may scale with the fifth or sixth power of the flow velocity. Thus, the noise associated with the ever-larger rotor diameter and higher local speeds due to increasing tower heights might impose limitations on the size of onshore-bound equipment in the future. This environmental restriction involves structural and material technical challenges already faced by the wind energy industry, which must meet challenging clean energy goals set by countries worldwide in order to fulfil greenhouse gas emissions limitations and global warming temperature limits proposed by the Paris Agreement and other subsequent sessions of the Conference of the Parties of the United Nations.By Joseph Youssif Saab Jr and Alexandre Martuscelli Faria, Brazil
- Details
- Category: Articles
 Opportunities to Recover Materials and Energy from End-of-Life Wind Turbine Blades
Opportunities to Recover Materials and Energy from End-of-Life Wind Turbine BladesAs wind turbines installed in the late 1990s and early 2000s begin to be decommissioned, it is important to consider sustainable options for handling their end-of-life materials. Recycling and other circular economy methods can reduce the material intensity of wind energy production, but composite blades are more difficult to recycle than many other major wind turbine components. Several circular economy strategies have been developed for processing composite materials, thereby enhancing the sustainability of electricity production from wind energy.
By Aubryn Cooperman, engineering analyst, National Wind Technology Center, NREL, USA
- Details
- Category: Articles
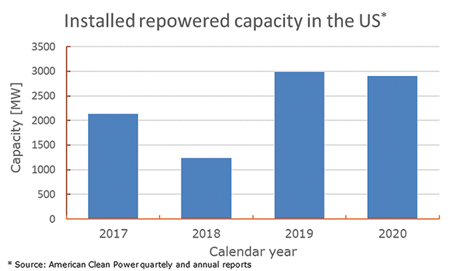 Key Technical Considerations to Ensure Successful and Sustainable Repowering
Key Technical Considerations to Ensure Successful and Sustainable RepoweringIn recent years, wind farm repowering has contributed an important fraction of overall US wind farm installations, as developers seek to capitalise on existing infrastructure, proven revenue streams, and tax credit eligibility. Partial repowering, as opposed to full repowering, remains the dominant form in the US market and typically involves reusing the existing foundation and towers, while replacing uptower components with new parts to attain higher performance and financial benefits from the asset. According to the ‘American Clean Power Market Report Fourth Quarter 2020’, partial repowering increased sharply from 2018 to 2019 and remained at roughly 3GW in 2020 (for reference, new US wind installations in 2020 accounted for roughly 17GW).
By Ali Ghorashi, Head of Section, Wind Independent Engineering, DNV, USA
- Details
- Category: Articles
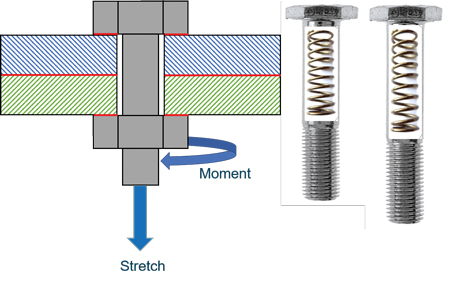 Correct Tension is Essential to Safety and Product Reliability
Correct Tension is Essential to Safety and Product ReliabilityAchieving and maintaining the right tension in bolted joints in wind turbines can help prevent system failures and associated repair costs. One loose bolt in a cluster of several hundred holding a structure together, often interdependently, can cause a domino effect that could, at worst, result in failure of the entire unit. As wind turbines continue to increase in size, the structures need to withstand ever higher centrifugal and bending forces, as well as vibrations – all factors that can affect the integrity of bolted joints. Correct bolt tensioning is, therefore, critical. But, accurate bolt tension is not only difficult to achieve, it can also be difficult to monitor. Danish engineering company R&D has developed an accurate system that uses both mechanical and ultrasonic measurements to determine the desired bolt tension in a way that also saves time. The solution can also digitally track individual bolts throughout their lifetime, ensuring the condition of the bolts is documented.
By Flemming Selmer Nielsen, Senior Specialist Engineer, R&D, Denmark
- Details
- Category: Articles
In Addition to Attractive Financial Returns, Investors Seek Environmental and Social Benefits
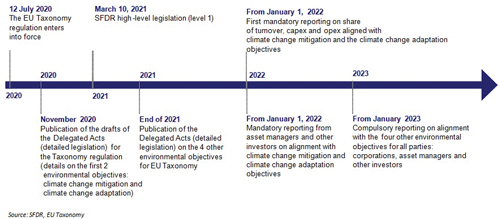 On 10 March 2021, the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation of the European Commission entered into force. This was the start for a relay race with several stages that will last several years and directly affect financing entities and indirectly affect project developers (see Figure 1 for the envisaged timeline). Developers will be forced by finance institutions to deliver assets that comply with the norm. If regulatory requirements are not met, the project will be less valuable or of no value at all. This article refers to the envisaged regulatory timeline and targeted objectives, which financiers must disclose, fulfil and monitor on an annual basis.
On 10 March 2021, the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation of the European Commission entered into force. This was the start for a relay race with several stages that will last several years and directly affect financing entities and indirectly affect project developers (see Figure 1 for the envisaged timeline). Developers will be forced by finance institutions to deliver assets that comply with the norm. If regulatory requirements are not met, the project will be less valuable or of no value at all. This article refers to the envisaged regulatory timeline and targeted objectives, which financiers must disclose, fulfil and monitor on an annual basis.By Rosa M. Tarragó, Strategy and Infrastructure Equity Specialist, Germany
Use of cookies
Windtech International wants to make your visit to our website as pleasant as possible. That is why we place cookies on your computer that remember your preferences. With anonymous information about your site use you also help us to improve the website. Of course we will ask for your permission first. Click Accept to use all functions of the Windtech International website.








