- Details
- Category: Articles
 Time Spent in Reconnaissance Critical for Offshore Wind’s Next Frontier
Time Spent in Reconnaissance Critical for Offshore Wind’s Next FrontierThe offshore wind market is accelerating rapidly as global political pressure mounts to transition to clean energy sources. New sites are being selected, many of which are in deep-water locations. This is possible as several floating foundations are now proven in full-scale offshore trials, so building on a commercial scale is theoretically achievable. It is clear that floating offshore wind represents the next frontier, but which floating structure will deliver the best levelised cost of energy? It is as much about the local port infrastructure as it is the floating foundation. With multiple solution providers developing various models across four main structure types, this article outlines some of the factors for consideration and explains how independent naval architecture consultancy can support informed decision-making.
Mark Goalen, Director of Offshore Engineering, Houlder, UK
- Details
- Category: Articles
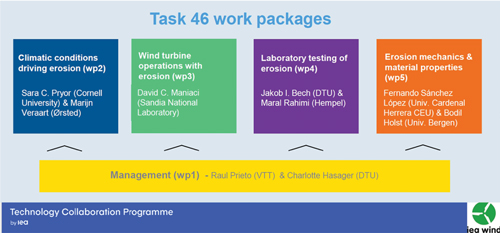 Introducing IEA Wind Task 46
Introducing IEA Wind Task 46Leading edge erosion of wind turbine blades has been identified as the main factor substantially reducing both blade lifetimes and energy output over time. Field repairs are costly due to lost availability and challenging access, work and weather conditions [1]. During the wind farm planning stage, the lack of validated methods to estimate the overall cost of erosion causes uncertainty in the investment decisions, again raising the levelised cost of energy.
By Raul Prieto, Charlotte Hasager, Sara C. Pryor, Marijn Veraart, David C. Maniaci, Jakob I. Bech, Maral Rahimi, Fernando Sánchez López, Bodil Holst and Sandro di Noi
- Details
- Category: Articles
 New Blade Coating Enhances Existing Lightning Protection Systems
New Blade Coating Enhances Existing Lightning Protection SystemsLightning damage stubbornly remains a major O&M expense for owner-operators in cost and frequency. Damage such as blade skin punctures, shell delamination, split trailing edges, and (less frequently) catastrophic damage to wind turbine blades is costly to repair and causes undesirable downtime. Even with the current mitigation systems in place, it is estimated that lightning damage costs the wind industry more than $ 100 million each year. Strikes are inevitable, and their frequency will only grow as turbines get taller, more onshore and offshore wind farms are developed, and our climate continues to change.
By Neal E. Fine, John A. Cooney and Christopher S. Szlatenyi, Arctura, Inc., USA
- Details
- Category: Articles
 Novel Methodology for Turbulent Wind Flow Simulations
Novel Methodology for Turbulent Wind Flow SimulationsWind turbine (WT) designers and wind farm developers are seeking improved tools for maximising power generation while minimising the life-cycle cost of their onshore and offshore projects. The industry recognises that key decisions required to achieve the lowest levelised cost of energy include wind farm: 1) site and WT model selection, 2) spacing or WT density, and 3) active control of each turbine’s operation considering blockage generated by interference of multiple turbulent wakes with the surroundings. Although the current consensus calls for spacing WTs at least seven rotor diameters apart, each WT design can have a different network effect that varies between sites having unique topography, wind patterns and other atmospheric conditions. As a consequence, designers with multiple site, hardware and network configuration options cannot rely on empirical rules of thumb to achieve optimal wind farms. Instead, design decisions should be guided by innovative computational fluid dynamics tools.
By Jacob Krispin and Joel Balbien, Vorcat, USA
- Details
- Category: Articles
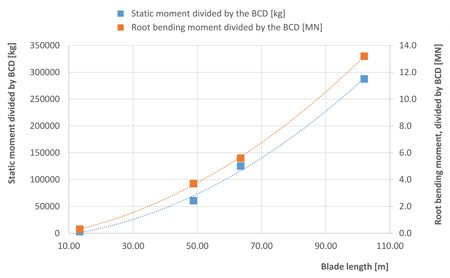 Optimisation of Blade Connections
Optimisation of Blade ConnectionsThe increasing length of recent large rotor blades with their growing mass and static moments brings new challenges with regard to the design of their blade connections. Since 2008, WINDnovation has designed approximately 250 blades and blade connections with very different individual solutions.
By Frank Seewald, Torsten Sadowski, Roland Stoer, WINDnovation Engineering Solutions, Germany
- Details
- Category: Articles
 A New Manufacturing Solution to Handle Rotor Hubs
A New Manufacturing Solution to Handle Rotor HubsEnercon is the first wind turbine manufacturer to break entirely new ground in handling rotor hubs on the assembly line – instead of using cranes and slings, Enercon relies on a compact turning table from RUD Ketten Rieger & Dietz, based in Aalen (Baden-Württemberg, Germany).
By Sabrina Deininger
- Details
- Category: Articles
 Fulfilling content resolution requirements
Fulfilling content resolution requirementsWhen discussing with potential partners about the visual inspection of wind turbines with drones, the first question that arises is which drone do you recommend? Inspecting wind turbines is not just about flying around the rotor blades and gathering high resolution pictures of everything. It is about image quality and supplementary metadata that improve the overall value of, and information about, an inspection flight, and processing and presenting the results in a manner that allows rotor blade experts to make precise decisions.
By Christian Raml, Head of Research and Development, Aero Enterprise, Austria
Use of cookies
Windtech International wants to make your visit to our website as pleasant as possible. That is why we place cookies on your computer that remember your preferences. With anonymous information about your site use you also help us to improve the website. Of course we will ask for your permission first. Click Accept to use all functions of the Windtech International website.








