- Details
- Category: Articles
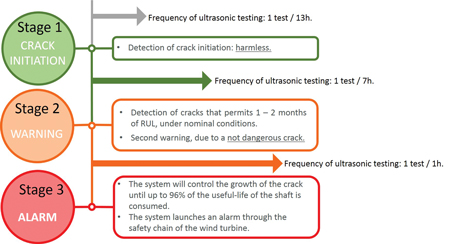 Autonomous Ultrasonic Condition Monitoring of Main Shafts
Autonomous Ultrasonic Condition Monitoring of Main ShaftsThe wind sector context and situation in Spain favours the life extension of wind farms over repowering, so the search for new and innovative solutions for extending the operating life of wind turbines, while keeping the maintenance costs at acceptable levels, is the focus of many wind sector stakeholders. The embedding of autonomous and smart sensing technologies in wind turbine components is a current technological trend that allows the online condition monitoring of turbine structural integrity and the optimisation of operational life and maintenance costs. In this context, Tecnalia presents LEO, an autonomous ultrasonic monitoring system for main shafts, which has been validated in the field and is currently in operation in several wind turbines in Spain.
By Jokin Rubio Botía and Nekane Galarza, Tecnalia Research & Innovation, Spain
- Details
- Category: Articles
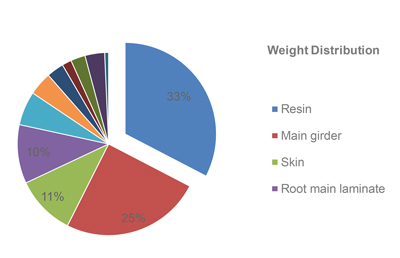 A Cost Reduction Opportunity?
A Cost Reduction Opportunity?A case study performed within We4Ce shows a blade cost reduction opportunity for polyester resins in rotor blades. However, will this cost reduction for the blade also lead to a lower cost of energy?
By Edo Kuipers, Engineering Manager, We4Ce, The Netherlands
- Details
- Category: Articles
 Variables, Margins and Their Impact
Variables, Margins and Their ImpactThe International Energy Agency’s Wind Technology Collaboration Programme Task 19 ‘International Recommendations for Ice Fall and Ice Throw Risk Assessments’, published in October 2018, gives a comprehensive overview of the necessary parts of a risk assessment and will hopefully form the basis for a future standard. Although it was obviously created with great care, the variables involved still leave considerable leeway for the results.
By Markus Drapalik, Institute of Safety and Risk Sciences, University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Vienna
- Details
- Category: Articles
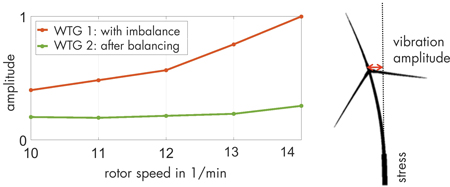 Load Monitoring and Lifetime Assessment of Wind Turbine Structures
Load Monitoring and Lifetime Assessment of Wind Turbine StructuresA wind turbine is one of the industrial structures with the highest vibration loads within its lifetime. It has to withstand up to 250 million load cycles within approximately 20 years. The vibration loads of wind turbines vary considerably depending on the location and operational mode of the wind turbine. Even two wind turbines in the same wind farm may differ significantly in their vibration loads. In the design phase, these loads can only roughly be determined, leading to potential reserves of a turbine’s lifetime during operation. Therefore, the structural monitoring of turbine towers is an essential part of controlling the lifetime of a wind turbine. In current operations on-site, the use of the retrofit solution SHM.Tower reveals that considerable reserves exist, allowing lifetime extension of turbine towers. Furthermore, lifetime-driven operation of wind turbines can be realised by using SHM.Tower, which is energy self-sufficient.
By Dr.-Ing. Carsten Ebert, Dr.-Ing. Manuel Eckstein, Dr.-Ing. Georg C Enss and Dipl.-Ing. Bernd Wölfel, Wölfel Wind Systems, Germany
- Details
- Category: Articles
 Combining Precast Concrete Parts and Steel Elements
Combining Precast Concrete Parts and Steel ElementsWind turbine performance is constantly improving. With this trend comes ever higher hub heights – a development that will also continue in the coming years. As turbine performance increases, political and economic demands regarding the profitability of wind turbines are likewise increasing. Turbines with capacities above 4MW will become the norm even for onshore sites. To effectively meet these challenges, innovative solutions from manufacturers are needed. Tower concepts such as the hybrid tower, which combines precast concrete parts and steel elements, are opening up new technical possibilities.
By Jürgen Joos, Chief Financial Officer, Max Bögl Wind, Germany
- Details
- Category: Articles
 Investigating the Impacts of Dynamic Mechanical Stresses on Fatigue Life of Dynamic Cables
Investigating the Impacts of Dynamic Mechanical Stresses on Fatigue Life of Dynamic CablesFloating platform wind turbines will require cables to run through the water column from their platform base at the water surface to the touchdown point on the seabed. This trajectory exposes the cable to dynamic environmental forces, such as waves and currents. The Offshore Renewable Energy Catapult (ORE Catapult) and the Industrial Doctoral Centre for Offshore Renewable Energy (IDCORE) have been investigating the impact of this dynamic marine environment on a dynamic cable’s fatigue life, with the aim of reducing uncertainty and improving the reliability of dynamic cables. The aim of this project is to allow more effective planned maintenance offshore through the prediction of a failure of a dynamic cable.
By David Young, IDCORE and ORE Catapult, and Lars Johanning, University of Exeter, UK
- Details
- Category: Articles
Variability Analyses and Considerations About Uncertainty for Long-Term Prediction
 The evolution of long-term wind resources is a key issue in the wind industry, especially in the context of energy yield assessments. Thus, analysing the evolution of the long-term wind trends in the past should allow a better appreciation of their variability and potentially the risk of experiencing periods with low wind resources in the future.
The evolution of long-term wind resources is a key issue in the wind industry, especially in the context of energy yield assessments. Thus, analysing the evolution of the long-term wind trends in the past should allow a better appreciation of their variability and potentially the risk of experiencing periods with low wind resources in the future.By Marion Jude, Eoltech, France
Use of cookies
Windtech International wants to make your visit to our website as pleasant as possible. That is why we place cookies on your computer that remember your preferences. With anonymous information about your site use you also help us to improve the website. Of course we will ask for your permission first. Click Accept to use all functions of the Windtech International website.








